- PRODUCTS
- COMPANY
- SUPPORT
- PRODUCTS
- BY TYPE
- BY MARKET
- COMPANY
- SUPPORT
Search No More — Marvell Breakthrough Questflo Network Search Engine Scales Up to 8 Million Flows
According to Cisco Forecasts¹, in three years mobile data traffic is projected to hit 11.2 exabytes per month (1 exabyte = 1 billion gigabytes) and will experience a 66 percent Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) from 2012 to 2017. 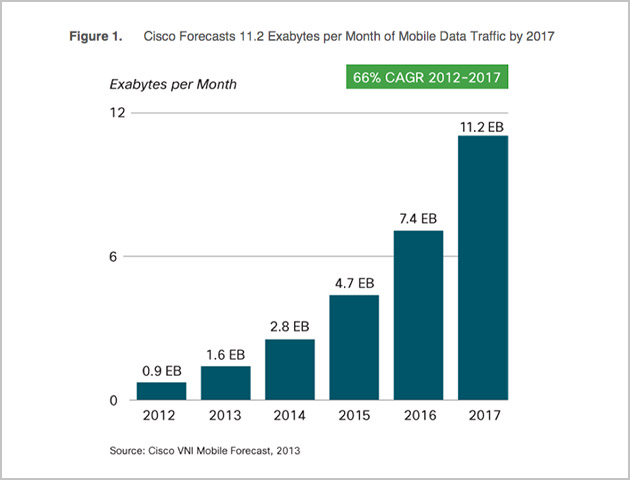 The demand for mobile Internet and Internet of Things (IoT) are amongst the drivers of this growth, as well as wearables and automotive connectivity. Not only is there an increase in the number of services and apps being used on mobile devices, but the number of devices per person has increased as well. For example, a user may stream video, access social networking or enterprise work applications, or run any number of apps from a single mobile phone, as well as own a tablet and wearable, like an iwatch, creating even more traffic. And all of this activity must be backhauled or aggregated to the Cloud at some point, leaving network providers and carriers in a constant quest to keep up with this explosive growth while providing high Quality of Service levels and enhanced security.
The demand for mobile Internet and Internet of Things (IoT) are amongst the drivers of this growth, as well as wearables and automotive connectivity. Not only is there an increase in the number of services and apps being used on mobile devices, but the number of devices per person has increased as well. For example, a user may stream video, access social networking or enterprise work applications, or run any number of apps from a single mobile phone, as well as own a tablet and wearable, like an iwatch, creating even more traffic. And all of this activity must be backhauled or aggregated to the Cloud at some point, leaving network providers and carriers in a constant quest to keep up with this explosive growth while providing high Quality of Service levels and enhanced security.
Today’s Ternary Content Addressable Memory (TCAM)-based solutions are unable to address the future scaling requirements of bandwidth and service to keep up with the explosive growth. The industry has been tinkering around with other network search engine solutions, yet none have been able to satisfy on all fronts: performance, density, power, cost, form factor and reliability. SRAM-based solutions to date have not offered the performance needed for such applications, and TCAMs that are added to gain more density become costly and run hot, exceeding the expected power and thermal and requirements of these networking systems.
Another driver is the shift from a forwarding paradigm to a flow-based management paradigm, where new services may not be IPv4- or IPv6 protocol-driven but protocol independent. New classes of Software Defined Networks (SDN) and Network Functions Virtualization (NFV) platforms will require such flexibilities at high capacity with deterministic latency and throughput to support these networks of the future.
Marvell recently announced, a major technology breakthrough with its Oct. 20 introduction of the Marvell Questflo™ 98TX1100, a groundbreaking Static Random Access Memory (SRAM)-based network search engine that delivers 4X capacity at 1/3 the power consumption to address the needs of next generation networking equipment. Targeted for the design of carrier and enterprise service/edge routers, security appliances, network probes, data center switches, servers, load balancers and the new classes of SDN and NFV platforms, the Questflo 98TX1100 is scalable to 8 million flow entries and can make 2.4 billion decisions per second. In addition to offering the performance and density needed, the Marvell solution operates at only 25W. When combined with a Marvell Xelerated 400 Gbps wire-speed network processor produces and ARMADA XP ARM-based embedded control processor, the new network search engine from Marvell provides a complete solution architecture to help next-generation equipment providers collectively support the exponential growth of mobile and IoT devices. 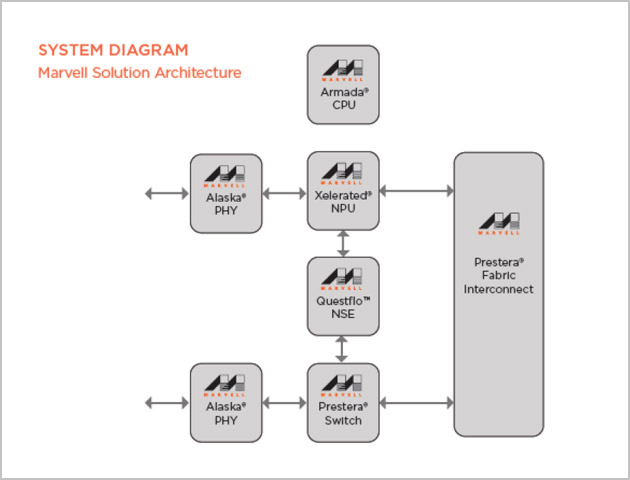 This Marvell breakthrough was summed up well by Bob Wheeler, Principal Analyst for Networking at The Linley Group: “As next-generation networking equipment adopts new paradigms based on highly flexible and highly scalable flow-based services, Marvell is entering the market as a credible supplier of network search technology. The magnitude of scaling required by these new equipment designs can only be realized using innovative new approaches like that represented by Questflo.”
This Marvell breakthrough was summed up well by Bob Wheeler, Principal Analyst for Networking at The Linley Group: “As next-generation networking equipment adopts new paradigms based on highly flexible and highly scalable flow-based services, Marvell is entering the market as a credible supplier of network search technology. The magnitude of scaling required by these new equipment designs can only be realized using innovative new approaches like that represented by Questflo.”
By addressing the needs of next-generation networking equipment on all fronts - performance, density, power, cost, form factor and reliability – we believe the search for the next-generation search engine is over, the answer is Questflo.
¹Cisco Visual Networking Index: Global Mobile Data Traffic Forecast Update, 2012–2017, © 2013 Cisco
Recent Posts
- The Golden Cable Initiative: Enabling the Cable Partner Ecosystem at Hyperscale Speed
- Marvell Named to America’s Best Midsize Employers 2026 Ranking
- Ripple Effects: Why Water Risk Is the Next Major Business Challenge for the Semiconductor Industry
- Boosting AI with CXL Part III: Faster Time-to-First-Token
- Marvell Wins Interconnect Product of the Year for Ara 3nm 1.6T PAM4 DSP
Archives
Categories
- 5G (10)
- AI (52)
- Cloud (24)
- Coherent DSP (12)
- Company News (108)
- Custom Silicon Solutions (11)
- Data Center (77)
- Data Processing Units (21)
- Enterprise (24)
- ESG (12)
- Ethernet Adapters and Controllers (11)
- Ethernet PHYs (3)
- Ethernet Switching (41)
- Fibre Channel (10)
- Marvell Government Solutions (2)
- Networking (46)
- Optical Modules (20)
- Security (6)
- Server Connectivity (37)
- SSD Controllers (6)
- Storage (23)
- Storage Accelerators (4)
- What Makes Marvell (48)
Copyright © 2026 Marvell, All rights reserved.
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Contact

