

By Kelvin Vivian, Director of Intellectual Property, Marvell
The term ‘innovation’ is frequently used in business today. For many, the term means providing ideas out of the blue, which lead to mind blowing discoveries and achievements.
out of the blue, which lead to mind blowing discoveries and achievements.
While this might be the perceived outcome of innovation, the reality is that true innovation can arise in a variety of different forms and can have any sizeable impact, and a healthy dose of creativity and idea sharing must be encouraged if businesses are to effectively harness the innovative potential of its employees.
At Marvell, we pride ourselves on working together collaboratively and creatively and this enables employees to be the most innovative versions of themselves, and such is what largely contributes to our sixth consecutive year of inclusion in the Clarivate Analytics Top 100 Global Innovators list.
Placement on the list has become the standard measure for innovation across the world and is recognized as a significant achievement. The award itself is based in part on global reach — we hold more than 9,000 patents worldwide — grant success rates and influence of patented technology, and it serves as a testament to Marvell’s culture of innovation and commitment to providing differentiated, breakthrough technology solutions.
While inclusion on this list provides a celebratory point of reflection for all of us at Marvell, it also is a reminder of the work that lays ahead of us and our colleagues across industry who, while competing, also share a common passion and goal, which simply put – is to make technology that makes life better. And in today’s market especially, it’s more important than ever that we and our partners continue to push the boundaries of innovation at every turn. As the physicist Albert Einstein said, “You can’t solve a problem on the same level that it was created. You have to rise above it to the next level.”
So while we extend our congratulations to colleagues and competitors alike, without whom there would be no yardstick to measure ourselves by and no goal to aim for; we can’t wait to see what new innovations and types of critical and creative thinking this year will bring.
See you all on the other side!
By Maen Suleiman, Senior Software Product Line Manager, Marvell
Following the success of the MACCHIATObin® development platform, which was released back in the spring, Marvell and technology partner SolidRun have now announced the next stage in the progression of this hardware offering. After drawing on the customer feedback received, a series of enhancements to the original concept have subsequently been made, so that these mini-ITX boards are much more optimized for meeting the requirements of engineers.
Marvell and SolidRun announce the availability of two new MACCHIATObin products that will supersede the previous release. They are the MACCHIATObin Single Shot and the MACCHIATObin Double Shot boards.
As before, these mini-ITX format networking community boards both feature the powerful processing capabilities of Marvell’s ARMADA® 8040 system-on-chip (SoC) and stay true to the original objective of bringing an affordable Arm-based development resource with elevated performance to the market. However, now engineers have a choice in terms of how much supporting functionality comes with it - thus making the platform even more attractive and helping to reach a much wider audience. 
Figure 1: MACCHIATObin Single Shot (left) and MACCHIATObin Double Shot (right)
The more streamlined MACCHIATObin Single Shot option presents an entry level board that should appeal to engineers with budgetary constraints. This has a much lower price tag than the original board, coming in at just $199. It comes with two 10G SFP+ connectors without the option of two 10G copper connectors, and also doesn’t come with default DDR4 DIMM as its predecessor, but still has a robust 1.6GHz processing speed.
This is complemented by the higher performance MACCHIATObin Double Shot. This unleashes the full 2GHz of processing capacity that can be derived from the ARMADA 8040, which relies on a 64-bit quad-core Arm Cortex-A72 processor core. 4GB of DDR4 DIMM is included. At only $399 it represents great value for money - costing only slightly more than the original, but with extra features and stronger operational capabilities being delivered. It comes with additional accessories that are not in the Single Shot package - including a power cable and a microUSB-to-USB cable.
Both the Single Shot and Double Shot versions incorporate heatsink and fan mechanisms in order to ensure that better reliability is maintained through more effective thermal management. The fan has an airflow of 6.7 cubic feet per minute (CFM) with low noise operation. A number of layout changes have been implemented upon the original design to better utilize the available space and to make the board more convenient for those using it. For example, the SD card slot has been moved to make it more accessible and likewise the SATA connectors are now better positioned, allowing easier connection of multiple cables. The micro USB socket has also been relocated to aid engineers.
A 3-pin UART header has been added to the console UART (working in parallel with FTDI USB-to-UART interface IC). This means that developers now have an additional connectivity option that they can utilize, making the MACCHIATObin community board more suitable for deployment in remote locations or where it needs to interface with legacy equipment (that do not have a USB port). The DIP switches have been replaced with jumpers, which again gives the boards greater versatility. The JTAG connector is not assembled by default, the PCI Express (PCIe) x4 slot has been replaced with an open PCIx4 slot so that it can accommodate a wider variety of different board options (like x8 and x16, as well as x4 PCIe) such as graphics processor cards, etc. to be connected. Furthermore, the fixed LED emitter has been replaced by one that is general purpose input/output (GPIO) controlled, thereby enabling operational activity to be indicated.
The fact that these units have the same form factor as the original, means that they offer a like-for-like replacement for the previous model of the MACCHIATObin board. Therefore existing designs that are already using this board can be upgraded to the higher performance MACCHIATObin Double Shot version or conversely scaled down to the MACCHIATObin Single Shot in order to reduce the associated costs.
Together the MACCHIATObin Double Shot and Single Shot boards show that the team at Marvell are always listening to our customer base and responding to their needs. Learning from the first MACCHIATObin release, we have been able to make significant refinements, and consequently develop two new very distinct product offerings. One that addresses engineers that are working to a tight budget, for which the previous board would not have been viable, and the other for engineers that want to boost performance levels.
By Marvell PR Team
Storage is the foundation for a data-centric world, but how tomorrow’s data will be stored is the subject of much debate. What is clear is that data growth will continue to rise significantly. According to a report compiled by IDC titled ‘Data Age 2025’, the amount of data created will grow at an almost exponential rate. This amount is predicted to surpass 163 Zettabytes by the middle of the next decade (which is almost 8 times what it is today, and nearly 100 times what it was back in 2010). Increasing use of cloud-based services, the widespread roll-out of Internet of Things (IoT) nodes, virtual/augmented reality applications, autonomous vehicles, machine learning and the whole ‘Big Data’ phenomena will all play a part in the new data-driven era that lies ahead.
Further down the line, the building of smart cities will lead to an additional ramp up in data levels, with highly sophisticated infrastructure being deployed in order to alleviate traffic congestion, make utilities more efficient, and improve the environment, to name a few. A very large proportion of the data of the future will need to be accessed in real-time. This will have implications on the technology utilized and also where the stored data is situated within the network. Additionally, there are serious security considerations that need to be factored in, too.
So that data centers and commercial enterprises can keep overhead under control and make operations as efficient as possible, they will look to follow a tiered storage approach, using the most appropriate storage media so as to lower the related costs. Decisions on the media utilized will be based on how frequently the stored data needs to be accessed and the acceptable degree of latency. This will require the use of numerous different technologies to make it fully economically viable - with cost and performance being important factors.
There are now a wide variety of different storage media options out there. In some cases these are long established while in others they are still in the process of emerging. Hard disk drives (HDDs) in certain applications are being replaced by solid state drives (SSDs), and with the migration from SATA to NVMe in the SSD space, NVMe is enabling the full performance capabilities of SSD technology. HDD capacities are continuing to increase substantially and their overall cost effectiveness also adds to their appeal. The immense data storage requirements that are being warranted by the cloud mean that HDD is witnessing considerable traction in this space.
There are other forms of memory on the horizon that will help to address the challenges that increasing storage demands will set. These range from higher capacity 3D stacked flash to completely new technologies, such as phase-change with its rapid write times and extensive operational lifespan. The advent of NVMe over fabrics (NVMf) based interfaces offers the prospect of high bandwidth, ultra-low latency SSD data storage that is at the same time extremely scalable.
Marvell was quick to recognize the ever growing importance of data storage and has continued to make this sector a major focus moving forwards, and has established itself as the industry’s leading supplier of both HDD controllers and merchant SSD controllers.
Within a period of only 18 months after its release, Marvell managed to ship over 50 million of its 88SS1074 SATA SSD controllers with NANDEdge™ error-correction technology. Thanks to its award-winning 88NV11xx series of small form factor DRAM-less SSD controllers (based on a 28nm CMOS semiconductor process), the company is able to offer the market high performance NVMe memory controller solutions that are optimized for incorporation into compact, streamlined handheld computing equipment, such as tablet PCs and ultra-books. These controllers are capable of supporting reads speeds of 1600MB/s, while only drawing minimal power from the available battery reserves. Marvell offers solutions like its 88SS1092 NVMe SSD controller designed for new compute models that enable the data center to share storage data to further maximize cost and performance efficiencies.
The unprecedented growth in data means that more storage will be required. Emerging applications and innovative technologies will drive new ways of increasing storage capacity, improving latency and ensuring security. Marvell is in a position to offer the industry a wide range of technologies to support data storage requirements, addressing both SSD or HDD implementation and covering all accompanying interface types from SAS and SATA through to PCIe and NMVe.  Check out www.marvell.com to learn more about how Marvell is storing the world’s data.
Check out www.marvell.com to learn more about how Marvell is storing the world’s data.
By Maen Suleiman, Senior Software Product Line Manager, Marvell
The adoption of multi-gigabit networks and planned roll-out of next generation 5G networks will continue to create greater available network bandwidth as more and more computing and storage services get funneled to the cloud. Increasingly, applications running on IoT and mobile devices connected to the network are becoming more intelligent and compute-intensive. However, with so many resources being channeled to the cloud, there is strain on today’s networks.
Instead of following a conventional cloud centralized model, next generation architecture will require a much greater proportion of its intelligence to be distributed throughout the network infrastructure. High performance computing hardware (accompanied by the relevant software), will need to be located at the edge of the network. A distributed model of operation should provide the needed compute and security functionality required for edge devices, enable compelling real-time services and overcome inherent latency issues for applications like automotive, virtual reality and industrial computing. With these applications, analytics of high resolution video and audio content is also needed.
Through use of its high performance ARMADA® embedded processors, Marvell is able to demonstrate a highly effective solution that will facilitate edge computing implementation on the Marvell MACCHIATObin™ community board using the ARMADA 8040 system on chip (SoC). At CES® 2018, Marvell and Pixeom teams will be demonstrating a fully effective, but not costly, edge computing system using the Marvell MACCHIATObin community board in conjunction with the Pixeom Edge Platform to extend functionality of Google Cloud Platform™ services at the edge of the network. The Marvell MACCHIATObin community board will run Pixeom Edge Platform software that is able to extend the cloud capabilities by orchestrating and running Docker container-based micro-services on the Marvell MACCHIATObin community board.
Currently, the transmission of data-heavy, high resolution video content to the cloud for analysis purposes places a lot of strain on network infrastructure, proving to be both resource-intensive and also expensive. Using Marvell’s MACCHIATObin hardware as a basis, Pixeom will demonstrate its container-based edge computing solution which provides video analytics capabilities at the network edge. This unique combination of hardware and software provides a highly optimized and straightforward way to enable more processing and storage resources to be situated at the edge of the network. The technology can significantly increase operational efficiency levels and reduce latency.
The Marvell and Pixeom demonstration deploys Google TensorFlow™ micro-services at the network edge to enable a variety of different key functions, including object detection, facial recognition, text reading (for name badges, license plates, etc.) and intelligent notifications (for security/safety alerts). This technology encompasses the full scope of potential applications, covering everything from video surveillance and autonomous vehicles, right through to smart retail and artificial intelligence. Pixeom offers a complete edge computing solution, enabling cloud service providers to package, deploy, and orchestrate containerized applications at scale, running on premise “Edge IoT Cores.” To accelerate development, Cores come with built-in machine learning, FaaS, data processing, messaging, API management, analytics, offloading capabilities to Google Cloud, and more. 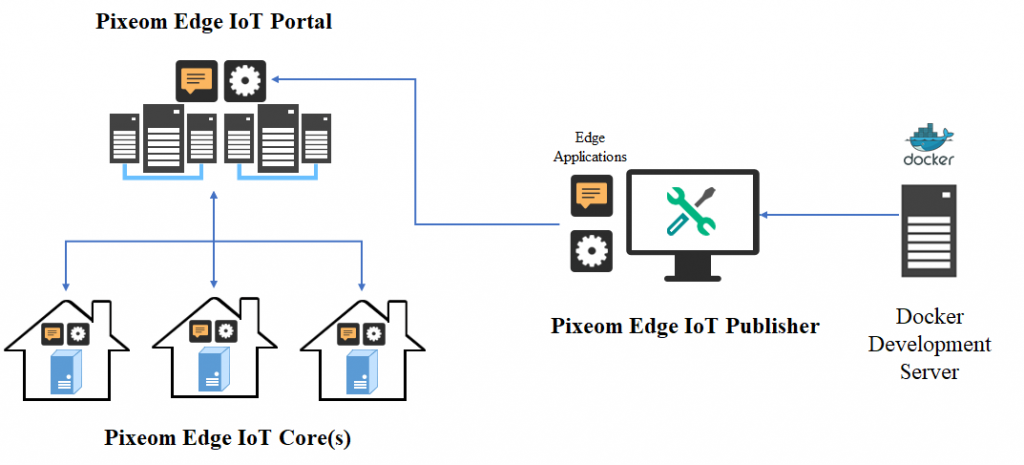 The MACCHIATObin community board is using Marvell’s ARMADA 8040 processor and has a 64-bit ARMv8 quad-core processor core (running at up to 2.0GHZ), and supports up to 16GB of DDR4 memory and a wide array of different I/Os. Through use of Linux® on the Marvell MACCHIATObin board, the multifaceted Pixeom Edge IoT platform can facilitate implementation of edge computing servers (or cloudlets) at the periphery of the cloud network. Marvell will be able to show the power of this popular hardware platform to run advanced machine learning, data processing, and IoT functions as part of Pixeom’s demo. The role-based access features of the Pixeom Edge IoT platform also mean that developers situated in different locations can collaborate with one another in order to create compelling edge computing implementations. Pixeom supplies all the edge computing support needed to allow Marvell embedded processors users to establish their own edge-based applications, thus offloading operations from the center of the network.
The MACCHIATObin community board is using Marvell’s ARMADA 8040 processor and has a 64-bit ARMv8 quad-core processor core (running at up to 2.0GHZ), and supports up to 16GB of DDR4 memory and a wide array of different I/Os. Through use of Linux® on the Marvell MACCHIATObin board, the multifaceted Pixeom Edge IoT platform can facilitate implementation of edge computing servers (or cloudlets) at the periphery of the cloud network. Marvell will be able to show the power of this popular hardware platform to run advanced machine learning, data processing, and IoT functions as part of Pixeom’s demo. The role-based access features of the Pixeom Edge IoT platform also mean that developers situated in different locations can collaborate with one another in order to create compelling edge computing implementations. Pixeom supplies all the edge computing support needed to allow Marvell embedded processors users to establish their own edge-based applications, thus offloading operations from the center of the network. 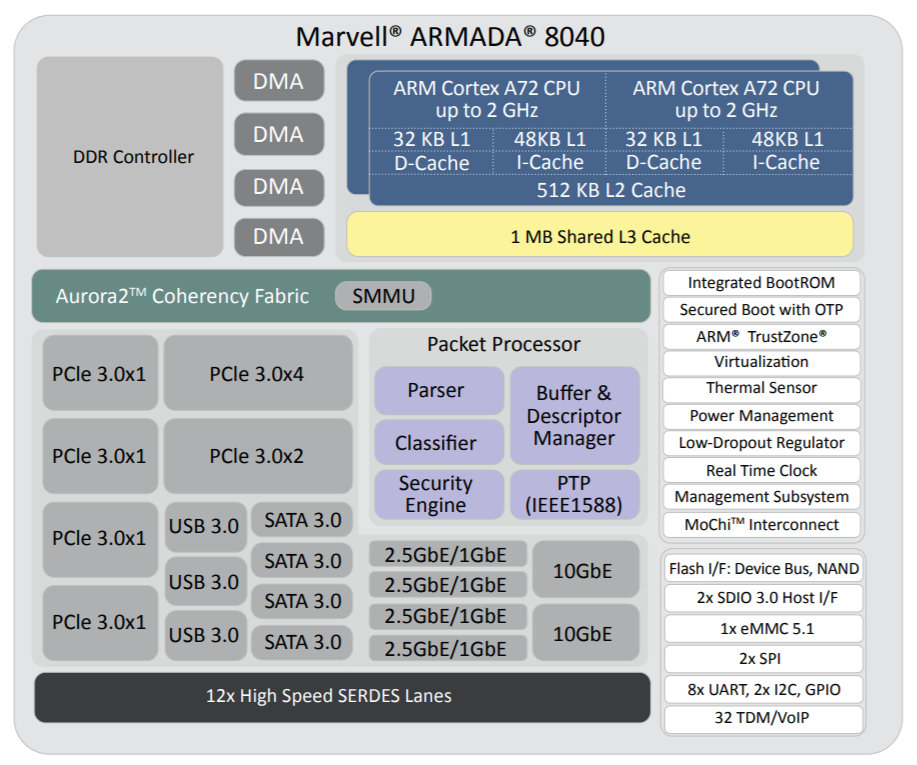 Marvell will also be demonstrating the compatibility of its technology with the Google Cloud platform, which enables the management and analysis of deployed edge computing resources at scale. Here, once again the MACCHIATObin board provides the hardware foundation needed by engineers, supplying them with all the processing, memory and connectivity required.
Marvell will also be demonstrating the compatibility of its technology with the Google Cloud platform, which enables the management and analysis of deployed edge computing resources at scale. Here, once again the MACCHIATObin board provides the hardware foundation needed by engineers, supplying them with all the processing, memory and connectivity required.
Those visiting Marvell’s suite at CES (Venetian, Level 3 - Murano 3304, 9th-12th January 2018, Las Vegas) will be able to see a series of different demonstrations of the MACCHIATObin community board running cloud workloads at the network edge. Make sure you come by!
By Marvell, PR Team
The data requirements of modern society are escalating at a relentless pace with new paradigms changing the way data is processed. The rapidly rising volume of data that is now being uploaded and downloaded from the cloud (such as HD video or equally data-intensive immersive gaming content) is putting incredible strain onto existing network infrastructure - testing both the bandwidth and data density speeds that are supported.
The onset of augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) will require access to considerable processing power, but at the same time mandate extremely low latency levels, to prevent lag effects. The widespread roll-out of IoT infrastructure, connected cars, robotics and industrial automation systems, to name a few, will also have uncompromising processing and latency demands that are simply not in line with current network architectures.
Transporting data from the network edge back to centralized servers (and vice versa) takes time, and hence adds an unacceptable level of latency to certain applications. All this will mean that fundamental changes need to be made. Rather than having all the processing resources located at the center of the network, a more distributed model is going to be needed in the future. Though the role of centralized servers will unquestionably still be important, this will be complemented by remote servers that are located at the edge of the network - thus making them closer to the users themselves, and thereby mitigating latency issues which is critical for time-sensitive data.
The figures on this speak for themselves. It is estimated that by 2020, approximately 45% of fog computing-generated data will be stored, processed, analyzed and subsequently acted upon either close to or at the edge of the network. Running in tandem with this, data centers will look to start utilizing in-storage processing. Here, in order to alleviate CPU congestion levels and mitigate network latency, data processing resources are going to start being placed closer to the storage drive. This, as a result, will dispense with the need to continuously transfer large quantities of data to and from storage reserves so that it can be processed, with processing tasks instead taking place inside the storage controller.
The transition from traditional data centers to edge-based computing, along with the onset of in-storage processing, will call for a new breed of processor devices. In addition to delivering the operational performance that high throughput, low latency applications will require, these devices will also need to meet the power, cost and space constraints that are going to characterize edge deployment.
Through the highly advanced portfolio of ARMADA® Arm-based multi-core embedded processors, Marvell has been able to supply the industry with processing solutions that can help engineers in facing the challenges that have just been outlined. These ICs combine high levels of integration, elevated performance and low power operation. Using ARMADA as a basis, the company has worked with technology partners to co-develop the MACCHIATObin™ and ESPRESSObin® community boards. The Marvell community boards, which each use 64-bit ARMADA processors, bring together a high-performance single-board computing platform and open source software for developers and designers working with a host of networking, storage and connectivity applications. They give users both the raw processing capabilities and the extensive array of connectivity options needed to develop proprietary edge computing applications from the ground up.
Incorporating a total of 6 MACCHIATObin boards plus a Marvell high density Prestera DX 14 port, 10 Gigabit Ethernet switch IC, the NFV PicoPod from PicoCluster is another prime example of ARMADA technology in action. This ultra-compact unit provides engineers with a highly cost effective and energy efficient platform upon which they can implement their own virtualized network applications. Fully compliant with the OPNFV Pharos specification, it opens up the benefits of NFV technology to a much broader cross section of potential customers, allowing everyone from the engineering teams in large enterprises all the way down to engineers who are working solo to rapidly develop, verify and deploy virtual network functions (VNFs) - effectively providing them with their own ‘datacenter on desktop’.
The combination of Marvell IoT enterprise edge gateway technology with the Google Cloud IoT Core platform is another way via which greater intelligence is being placed at the network periphery. The upshot of this will be that the estimated tens of billions of connected IoT nodes that will be installed over the course of the coming years can be managed in the most operationally efficient manner, offloading much of the workload from the core network’s processing capabilities and only utilizing them when it is completely necessary.  Check out www.marvell.com to learn more about how Marvell is processing the world’s data.
Check out www.marvell.com to learn more about how Marvell is processing the world’s data.